Chemical Thinking Parallel Dilution Set v1.4 1 Parallel Vdiluent Dilution VS. A dilution set is a group of solutions prepared by diluting a substance dissolved in a liquid. For the vast majority of cases the objective of building a dilution set is to create dilutions of defined concentration from a single “stock” or original solution of. Serial Vs Parallel Dilutions. The setup of IC5. The use of the Echo Liquid Handler eliminates these errors, enabling discoveries that would have been missed by other methods. By coupling the Echo Liquid Handler with Labcyte Automation and Echo Software Applications, IC5. Serial Vs Parallel Dilution SECOND: Also use a serial dilution when the dilution factor is so large that the amount of stock solution needed to make the dilution in one step (using the formula C 1V 1 = C 2V 2) is too small to measure accurately. Remember that the smallest volume you can measure with the micropipettors is 2 μL.
Learning Objective
- Calculate the concentration of a diluted solution.
Key Points
- Most commonly, a solution’s concentration is expressed in terms of mass percent, mole fraction, molarity, molality, and normality. When calculating dilution factors, it is important that the units of volume and concentration remain consistent.
- Dilution calculations can be performed using the formula M1V1 = M2V2.
- A serial dilution is a series of stepwise dilutions, where the dilution factor is held constant at each step.
Terms

- dilutiona solution that has had additional solvent, such as water, added to make it less concentrated
- serial dilutionstepwise dilution of a substance in solution
Dilution refers to the process of adding additional solvent to a solution to decrease its concentration. This process keeps the amount of solute constant, but increases the total amount of solution, thereby decreasing its final concentration. Dilution can also be achieved by mixing a solution of higher concentration with an identical solution of lesser concentration. Diluting solutions is a necessary process in the laboratory, as stock solutions are often purchased and stored in very concentrated forms. For the solutions to be usable in the lab (for a titration, for instance), they must be accurately diluted to a known, lesser concentration.
The volume of solvent needed to prepare the desired concentration of a new, diluted solution can be calculated mathematically. The relationship is as follows:

[latex]M_1V_1=M_2V_2[/latex]
M1 denotes the concentration of the original solution, and V1 denotes the volume of the original solution; M2 represents the concentration of the diluted solution, and V2 represents the final volume of the diluted solution. When calculating dilution factors, it is important that the units for both volume and concentration are the same for both sides of the equation.
Example
- 175 mL of a 1.6 M aqueous solution of LiCl is diluted with water to a final volume of 1.0 L. What is the final concentration of the diluted solution?
- [latex]M_1V_1=M_2V_2[/latex]
- (1.6 M)(175 mL) = M2(1000 mL)
- M2 = 0.28 M
Serial Dilutions
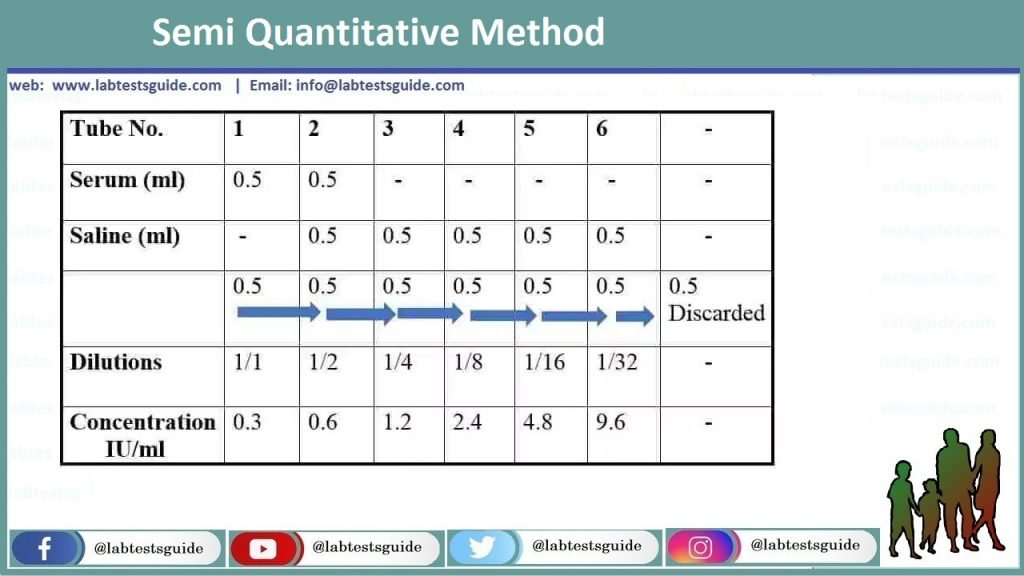
Serial dilutions involve diluting a stock or standard solution multiple times in a row. Typically, the dilution factor remains constant for each dilution, resulting in an exponential decrease in concentration. For example, a ten-fold serial dilution could result in the following concentrations: 1 M, 0.1 M, 0.01 M, 0.001 M, and so on. As is evidenced in this example, the concentration is reduced by a factor of ten in each step. Serial dilutions are used to accurately create extremely diluted solutions, as well as solutions for experiments that require a concentration curve with an exponential or logarithmic scale. Serial dilutions are widely used in experimental sciences, including biochemistry, pharmacology, microbiology, and physics.
Show SourcesBoundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
http://www.boundless.com/
Boundless Learning
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/serial%20dilution
Wikipedia
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/dilution
Wiktionary
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serial_dilution
Wikipedia
CC BY-SA 3.0.
Serial Vs Parallel Dilution
http://cnx.org/content/m17123/latest/
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Dilution-concentration_simple_example.jpg
Wikimedia
CC BY-SA.
- Posted in:Admin
- 13/04/18
Contents • • • • Parallel Data [ ] The parallel port on modern computer systems is an example of a parallel communications connection. The parallel port has 8 data wires, and a large series of ground wires and control wires. IDE hard-disk connectors and PCI expansion ports are another good example of parallel connections in a computer system. Serial Data [ ] The serial port on modern computers is a good example of serial communications. Serial ports have either a single data wire, or a single differential pair, and the remainder of the wires are either ground or control signals. USB, FireWire, SATA and PCI Express are good examples of other serial communications standards in modern computers.
Serial Dilution in Microbiology: Calculation. An example serial dilution using the easiest method. In Microbiology: Calculation, Method & Technique. Dilutions: Explanations and Examples of Common Methods. There are many ways of expressing concentrations and dilution. Autocad Lisp Steel Sections Properties there. Serial Dilutions.
Which is Better? [ ] It is a natural question to ask which one of the two transmission methods is better.
Serial Vs Parallel Dilution Method Formula
At first glance, it would seem that parallel ports should be able to send data much faster than serial ports. Logitech Mk300 Driver Vista more. Let's say we have a parallel connection with 8 data wires, and a serial connection with a single data wire.
Simple arithmetic seems to show that the parallel system can transmit 8 times as fast as the serial system. However, parallel ports suffer extremely from inter-symbol interference (ISI) and noise, and therefore the data can be corrupted over long distances. Also, because the wires in a parallel system have small amounts of capacitance and mutual inductance, the bandwidth of parallel wires is much lower than the bandwidth of serial wires. We all know by now that an increased bandwidth leads to a better bit rate.
We also know that less noise in the channel means we can successfully transmit data reliably with a higher Signal-to-Noise Ratio, SNR. If, however, we bump up the power in a serial connection by using a differential signal with 2 wires (one with a positive voltage, and one with a negative voltage), we can use the same amount of power, have twice the SNR, and reach an even higher bitrate without suffering the effects of noise. USB cables, for instance, use shielded, differential serial communications, and the USB 2.0 standard is capable of data transmission rates of 480Mbits/sec! In addition, because of the increased potential for noise and interference, parallel wires need to be far shorter than serial wires. Consider the standard parallel port wire to connect the PC to a printer: those wires are between 3 and 4 feet long, and the longest commercially available is typically 25 meter(75 feet). Now consider Ethernet wires (which are serial, and typically unshielded twisted pair): they can be bought in lengths of 100 meters (300 feet), and a 300 meters (900 feet) run is not uncommon!
UART, USART [ ] A Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) peripheral is used in embedded systems to convert bytes of data to bit strings which may be transmitted asynchronously using a serial protocol like RS-232. A Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (USART) peripheral is just like a UART peripheral, except there is also a provision for synchronous transmission by means of a clock signal which is generated by the transmitter.
Serial Dilution Experiment
• On the use of the serial dilution culture method to enumerate viable phytoplankton in natural communities of plankton subjected to ballast water treatment • There are two situations where serial dilutions should be used rather than parallel dilutions: FIRST: Use a serial dilution when you need several solutions of the same solute and there is a constant dilution factor. Therefore, this series has a constant dilution factor of 10. • THE INDICATOR DILUTION METHOD: ASSUMPTIONS AND APPLICATIONS TO BRAIN UPTAKE Olaf B. Paulson and Marianne M. Hertz State University Hospital, Copenhagen, Denmark • ARQ 197 (Tivantinib) is a novel and selective human c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with a minmal IC50 of 0.1 μM. Find all the information about ARQ 197.
Comments are closed.